다차원 배열
다차원 배열이란 2차원 이상의 배열을 의미하며, 배열 요소로 또 다른 배열을 가지는 배열을 의미합니다.

이런식으로 int arr2[2] [5]를 해준다는 것은
5개짜리 배열이 2개 있다는 소리입니다.
3차원 배열도 있습니다.
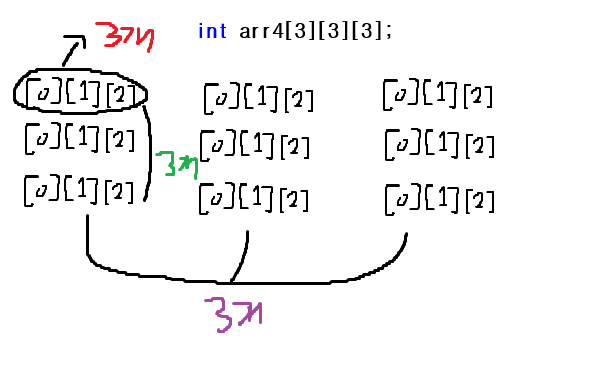
선언하는 방법은
int arr2[2][5] = {
{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }
}; // 2차원 배열
int arr4[3][3][3] = {
{
{1,2,3},
{1,2,3},
{1,2,3}
},
{
{1,2,3},
{1,2,3},
{1,2,3}
},
{
{1,2,3},
{1,2,3},
{1,2,3}
}
}; // 3차원 배열
2차원 배열을 사용하는 방법입니다.
int arr3[4][2] = {
{1,2},
{3,4},
{5,6},
{7,8}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
printf("2차원 배열 (%d, %d) 의 값 : %d\n", i, j, arr3[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}

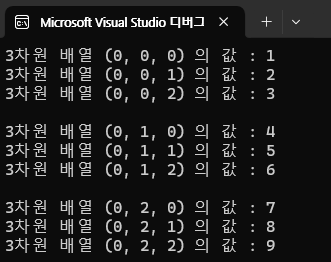
3차원 배열을 사용하는 방법입니다.
int arr4[3][3][3] = {
{
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9}
},
{
{11,12,13},
{14,15,16},
{17,18,19}
},
{
{21,22,23},
{24,25,26},
{27,28,29}
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
{
printf("3차원 배열 (%d, %d, %d) 의 값 : %d\n", i, j, k,arr4[i][j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}

프로젝트 동물 뒤집기
카드를 뒤집어서 같은 짝을 찾는 게임입니다.

#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int arrayAnimal[4][5]; // 20장의 카드 (4x5)
int checkAnimal[4][5]; // 뒤집혔는지 여부 확인
char* strAnimal[10];
void initAnimalArray();
void initAnimalName();
void shuffleAnimal();
int getEmptyPosition();
int conv_pos_x(int x);
int conv_pos_y(int y);
void printAnimals();
void printQuestion();
int main(void)
{
srand(time(NULL));
initAnimalArray();
initAnimalName();
shuffleAnimal();
int failCount = 0; // 실패 횟수
while (1)
{
int select1 = 0; // 처음 수
int select2 = 0; // 두번째 수
printAnimals(); // 동물 위치 출력
printQuestion(); // 문제 출력 (카드 지도)
printf("뒤집을 카드를 2개 고르세요 : ");
scanf_s("%d %d", &select1, &select2);
if (select1 == select2)
continue;
// 좌표에 해당하는 카드를 뒤집어 보고 같은지 안같은지 확인
// 정수 좌표를 (x,y) 로 변환
int firstSelect_x = conv_pos_x(select1);
int firstSelect_y = conv_pos_y(select1);
int secondSelect_x = conv_pos_x(select2);
int secondSelect_y = conv_pos_y(select2);
// 같은 동물인 경우
if ((checkAnimal[firstSelect_x][firstSelect_y] == 0
&& checkAnimal[secondSelect_x][secondSelect_y] == 0)
&&
(arrayAnimal[firstSelect_x][firstSelect_y]
== arrayAnimal[secondSelect_x][secondSelect_y])
)
{
printf("\n\n 빙고 ! : %s 발견\n\n", strAnimal[arrayAnimal[firstSelect_x][firstSelect_y]]);
checkAnimal[firstSelect_x][firstSelect_y] = 1;
checkAnimal[secondSelect_x][secondSelect_y] = 1;
}
else
{
printf("\n\n 땡!! (틀렸거나, 이미 뒤집힌 카드입니다.)\n");
printf("%d : %s\n", select1, strAnimal[arrayAnimal[firstSelect_x][firstSelect_y]]);
printf("%d : %s\n", select2, strAnimal[arrayAnimal[secondSelect_x][secondSelect_y]]);
printf("\n\n");
failCount++;
}
// 모든 동물을 찾았는지 여부, 1 : 참, 0 : 거짓
if (foundAllAnimals() == 1)
{
printf("\n\n 축하합니다 ! 모든 동물을 다 찾았네요 ! \n");
printf("지금까지 총 %d 번 실수하였습니다.\n", failCount);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
void initAnimalArray()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
arrayAnimal[i][j] = -1;
}
}
}
void initAnimalName()
{
strAnimal[0] = "원숭이";
strAnimal[1] = "돼지";
strAnimal[2] = "고양이";
strAnimal[3] = "강아지";
strAnimal[4] = "코끼리";
strAnimal[5] = "기린";
strAnimal[6] = "낙타";
strAnimal[7] = "하마";
strAnimal[8] = "호랑이";
strAnimal[9] = "타조";
}
void shuffleAnimal()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
int pos = getEmptyPosition();
int x = conv_pos_x(pos);
int y = conv_pos_y(pos);
arrayAnimal[x][y] = i;
}
}
}
// 좌표에서 빈 공간 찾기
int getEmptyPosition()
{
while (1)
{
int randPos = rand() % 20; // 0 ~ 19 사이의 숫자 반환
int x = conv_pos_x(randPos);
int y = conv_pos_y(randPos);
if (arrayAnimal[x][y] == -1)
{
return randPos;
}
}
return 0;
}
int conv_pos_x(int x)
{
// 19 -> (3,4)
return x / 5;
}
int conv_pos_y(int y)
{
// 19 -> 19 / 5 ? 몫은 3, 나머지 4
return y % 5; // y를 5로 나눈 나머지 값
}
void printAnimals() // 동물 위치 출력
{
printf("\n======================================\n\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%8s",strAnimal[arrayAnimal[i][j]]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n======================================\n\n");
}
void printQuestion() // 문제 출력 (카드 지도)
{
printf("\n\n(문제)\n");
int seq = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
// 카드를 뒤집어서 정답을 맞혔으면 '동물 이름'
if (checkAnimal[i][j] != 0)
{
printf("%8s", strAnimal[arrayAnimal[i][j]]);
}
else
{
printf("%8d", seq);
}
seq++;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int foundAllAnimals()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (checkAnimal[i][j] == 0)
{
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1; // 모두 다 찾음
}



'C' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C언어 (12) (0) | 2024.11.23 |
|---|---|
| C언어(11) (0) | 2024.11.21 |
| C언어(9) (0) | 2024.11.19 |
| C언어(8) 기초8 (0) | 2024.11.18 |
| C언어(7) 기초7 (0) | 2024.11.16 |